The seventh CACHE challenge is focused on PGK2, a kinase and a potential contraceptive drug target effecting sperm bioenergetics that is being actively pursued within the Gates Foundation non-hormonal contraceptive program. This challenge is supported by unpublished data provided by program members Damian Young and Kevin MacKenzie (BCM), Neelagandan Kamariah (inStem), Levon Halabelian and Hui Peng (SGC-Toronto), and Tim Willson (SGC-UNC).
CACHE participants are tasked with identifying orthosteric inhibitors that are selective for PGK2 over its close homologue PGK1, a glycolytic enzyme with available crystal structures in the PDB. All sidechains in the ligand binding pocket are conserved except for Y242 (PGK2) vs F242 (PGK1) and A255 (PGK2) vs T255 (PGK1) at the edge of the pocket.
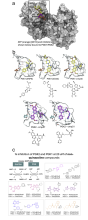
Figure 1: Structural chemistry of PGK1/2 inhibition. The ATP-bound structure has the PDB identifier 2X15 (a). Overview of structures (b) and ligands (c), most unpublished, that may inform the computational prediction of non-quinazoline inhibitors selective for PGK2 vs PGK1.
Available structural data include ATP-bound and ligand-bound hPGK1, ATP bound and apo mPGK2, and hPGK2 bound to two selective PGK2 quinazoline inhibitors (compound 21 and compound 47). hPGK1 bound to a selective quinazoline PGK1 inhibitor (compound 45) is also provided. Atomic coordinates and electron density files are available here.
Preliminary data on unpublished non-quinazoline ligands with some selectivity for PGK2 are shown (Figure 1c).
CACHE participants are also provided with 1388 hPGK2 hit candidates from a DNA-encoded library (DEL) screen (5 reads or more) that are not enriched in a hPGK1 screen. These compounds have not been tested off-DNA. As typical for DEL data, the signal-to-noise ratio is expected to be low and should be interpreted accordingly (ex: Montoya et al 2025).
The quinazoline series is well-advanced and will be published soon. CACHE #7 participants are therefore asked to discover SELECTIVE hPGK2 inhibitors that DO NOT contain a quinazoline.
Last date to apply is: